Cryptocurrency – Explanation and Concept Cryptocurrency, often referred to as crypto-currency or simply crypto, is any type of digital or virtual currency that utilizes cryptography to secure transactions. Unlike traditional currencies, cryptocurrencies operate independently of any central issuing or regulatory authority. Instead, they rely on a decentralized system to record transactions and create new units.
Understanding Cryptocurrency Cryptocurrency serves as a digital payment system that doesn’t require banks to authenticate transactions. It operates as a peer-to-peer system, allowing individuals worldwide to send and receive payments without intermediaries. Rather than physical money exchanged in person, cryptocurrency transactions exist solely as digital entries in an online database, with transfers recorded in a public ledger. Cryptocurrency holdings are stored in digital wallets.
The term “cryptocurrency” stems from its utilization of encryption to validate transactions, incorporating advanced coding for the secure storage and transmission of cryptocurrency data between wallets and public ledgers. The primary goal of encryption is to ensure security and safeguard transactions.
Bitcoin, established in 2009, stands as the first cryptocurrency and remains the most widely recognized. Much of the fascination surrounding cryptocurrencies involves trading for profit, with speculators sometimes causing significant price fluctuations.
How does Cryptocurrency Operate?
Cryptocurrencies operate on a distributed public ledger known as the blockchain, which serves as a comprehensive record of all transactions maintained and updated by currency holders.
Units of cryptocurrency are generated through a process called mining, which entails employing computational power to solve complex mathematical problems that yield coins. Alternatively, users can purchase cryptocurrencies from brokers and manage them using cryptographic wallets.
Owning cryptocurrency doesn’t entail physical possession; rather, it grants ownership of a key facilitating the transfer of records or units of measure between individuals without reliance on a trusted third party.
While Bitcoin has existed since 2009, cryptocurrencies and the applications of blockchain technology continue to evolve financially, with anticipated expansion into diverse sectors. Eventually, transactions involving bonds, stocks, and other financial assets could transpire utilizing this technology.

Examples of Cryptocurrencies A myriad of cryptocurrencies exists, with some of the most prominent including:
Bitcoin: Pioneered in 2009, Bitcoin remains the foremost cryptocurrency, founded by Satoshi Nakamoto, whose true identity remains undisclosed.
Ethereum: Introduced in 2015, Ethereum functions as a blockchain platform featuring its cryptocurrency, Ether (ETH), and ranks as the second most prevalent cryptocurrency after Bitcoin.
Litecoin: Bearing resemblance to Bitcoin, Litecoin prioritizes rapid innovation, boasting faster payments and enhanced transaction capabilities.
Ripple: Established in 2012, Ripple operates as a distributed ledger system capable of tracking various transaction types beyond cryptocurrencies, collaborating with diverse banks and financial institutions.
Non-Bitcoin cryptocurrencies collectively referred to as “altcoins” differentiate from the original.
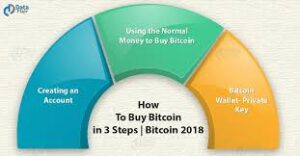
How to Acquire Cryptocurrency Interested in purchasing cryptocurrency securely? Typically, the process entails three steps:
Step 1: Platform Selection Choose a platform, either a conventional broker or a dedicated cryptocurrency exchange, based on your preferences. Consider factors such as offered cryptocurrencies, fees, security features, and available educational resources.
Step 2: Account Funding Once a platform is selected, fund your account to commence trading. Most exchanges facilitate cryptocurrency purchases using fiat currencies via debit or credit cards, though methods may vary.
Step 3: Placing Orders Execute trades through the chosen platform’s web or mobile interface by specifying the order type, quantity, and confirmation. Additionally, consider alternative investment avenues such as payment services, Bitcoin trusts, mutual funds, or blockchain stocks.
Securing Cryptocurrency Following acquisition, safeguard cryptocurrency holdings against hacks or theft by storing them in crypto wallets. These can be physical devices or online software, categorized as hot or cold wallets based on their online or offline nature.
Utilizing Cryptocurrency for Transactions Although initially conceived as a medium for daily transactions, Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies have yet to achieve widespread acceptance for such purposes. Nevertheless, several retailers, e-commerce platforms, luxury goods vendors, car dealerships, and insurance providers now accept cryptocurrency payments, albeit on a limited scale.
Risks and Precautions Cryptocurrency transactions are susceptible to fraud and scams, including fake websites, virtual Ponzi schemes, fraudulent endorsements, romance scams, and hacking. While blockchain technology enhances security, cryptocurrencies remain vulnerable to exploitation due to their decentralized nature.
Investing Prudently Should you choose to invest in cryptocurrencies, exercise caution and diligence. Research exchanges, understand storage methods, diversify investments, and prepare for market volatility. Remember, cryptocurrency investment entails risk, and prudent decision-making is essential to mitigate potential losses.
In conclusion, while cryptocurrency presents an enticing investment opportunity, it also demands thorough research, informed decision-making, and prudent risk management to ensure a safe and rewarding experience.

